ProntoGUI™ Box Layout Model
Introduction
It is common for GUI libraries or frameworks to offer flexibility in how widgets are sized and positioned on the screen in an absolute sense, or in a relative to other widgets. This document describes a model that ProntoGUI uses for layout and the relationships to embodiment properties defined in the ProntoGUI specification.
The Model
The model for layout is similar to the CSS Box Model and adds support for alignment and fixed positioning of a primitive.
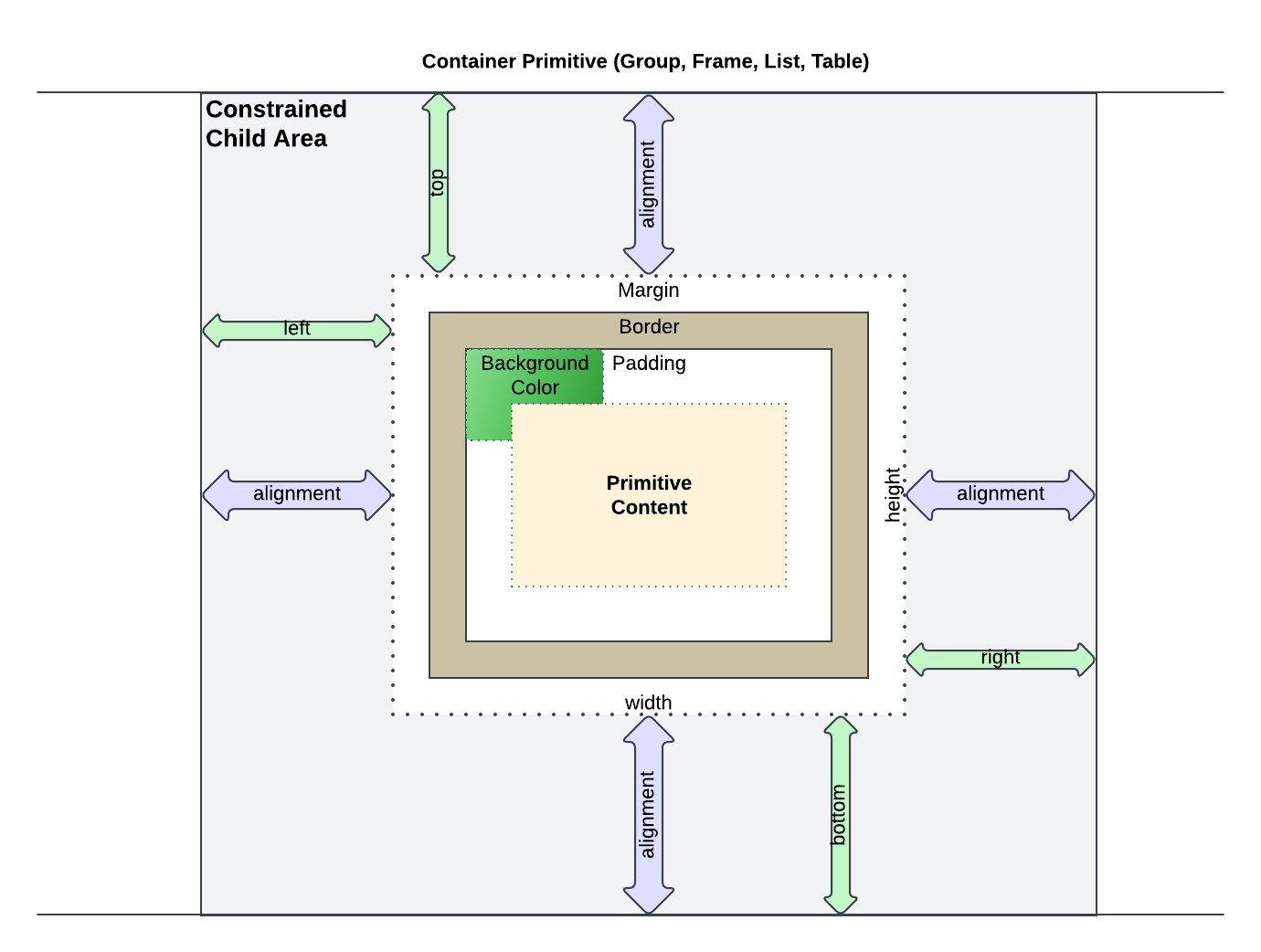
Constrained Child Area (CCA)
The Constrained Child Area, CCA for short, is the space provided by the containing primitive, inside which the primitive will be rendered. For example, it could be an item inside a Group or Frame, a List item, or a Table cell. During rendering, the constrained area is determined by the container, passed down to the primitive, the primitive decides how much of the CCA it will consume and returns this information back to the container, which will then position the primitive accordingly. This algorithm comes from how Flutter goes about laying out and rendering widgets (see resources section).
Embodiment Settings
This section discusses the embodiment settings which every primitive can possess to customize how it is laid out in the CCA.
Alignment Settings
Alignment settings may be specified for child primitives of a Frame, when the layoutMethod setting is set to flow. These settings have no effect for other layout methods.
horizontalAlignment
Specifies how the primitive is aligned and sized horizontally within the child area.
Valid settings are: * left * center * right * expand
verticalAlignment
Specifies how the primitive is aligned and sized vertically within the child area.
Valid settings are: * top * middle * bottom * expand
Border Settings
borderLeft, borderRight, borderTop, borderBottom
The size of the border in logical pixels for each side of primitive. The default value is 0 for no border. These take precedence over borderAll.
borderAll
The size of the border in logical pixels for all sides of the primitive. Individual sides can be overriden using borderLeft, borderRight, and so on.
borderColor
The color of the border expressed as an ARGB value.
borderStyle (TBD)
The style of border. Valid settings are: * outlined
Color Settings
backgroundColor
The color displayed behind the primitive content and inside the padding area. Background color will show through any transparent portions of the primitive content.
Position Settings
Position settings may be specified for child primitives of a Frame, when the layoutMethod setting is set to positioned. These settings have no effect for other layout methods.
left
The positioning of the primitive relative to the left edge of the CCA. This setting takes precedence over the right setting.
top
The positioning of the primitive relative to the top edge of the CCA. This setting takes precedence over the bottom setting.
right
The positioning of the primitive’s right side relative to the left edge of the CCA. If this value is negative then the magnitude specifies the positioning relative to the right edge of the CCA.
bottom
The positioning of the primitive’s bottom side relative to the top edge of the CCA. If this value is negative then the magnitude specifies the positioning relative to the bottom edge of the CCA.
The left, width, right
Size Settings
width
The intended width of the primitive, including the bounded size of the primitive, padding, border, and margin.
Margin Settings
marginLeft, marginRight, marginTop, marginBottom
The amount of margin in logical pixels for the each side of the primitive. The default value is 0 for no margin. These take precedence over marginAll.
marginAll
The amount of margin in logical pixels for all sides of the primitive. Individual sides can be overriden using marginLeft, marginRight, and so on.
Padding Settings
paddingLeft, paddingRight, paddingTop, paddingBottom
The amount of padding in logical pixels for the each side of the primitive. The default value is 0 for no padding. These take precedence over paddingAll.
paddingAll
The amount of padding in logical pixels for all sides of the primitive. Individual sides can be overriden using paddingLeft, paddingRight, and so on.
Bounded Versus Unbounded Primitives
Depending on its nature, a primitive can have a bounded or an unbounded size.
Primitives that always have a bounded size are: * Check * Choice * Command * ExportFile * Icon * ImportFile * NumericField * TextField * Timer * Tristate
Primitives that are unbounded are: * Group * Frame * List * Table
Additional Resources
- Understanding Flutter constraints https://docs.flutter.dev/ui/layout/constraints
- Flutter: The Advanced Layout Rule Even Beginners Must Know https://medium.com/flutter-community/flutter-the-advanced-layout-rule-even-beginners-must-know-edc9516d1a2
- CSS Box Model https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_boxmodel.asp